🔗 What is Blockchain?
Blockchain is a decentralized digital ledger that records transactions in a secure, transparent, and immutable way. Instead of being stored in one central place, it is distributed across many computers (nodes) worldwide.
🏗 How Does Blockchain Work?
- Transactions are grouped into blocks.
- Each block contains:
- A list of transactions
- A unique identifier (hash)
- The hash of the previous block (creating a chain)
- Once a block is verified, it is added to the blockchain.
🔢 Understanding Hashing
A hash function is a mathematical function that converts input data into a fixed-length string of characters and something that makes them special is that the slightest change in input creates a completely different hash.
| Input | SHA-256 Hash |
|---|---|
| Hello | 185F8DB32271FE25F561A6FC938B2E264306EC304EDA518007D1764826381969 |
| hello | 2CF24DBA5FB0A30E26E83B2AC5B9E29E1B161E5C1FA7425E73043362938B9824 |
Key Insight: Changing just one character drastically changes the hash.
Try It Yourself!
Try our Hashing Tool, enter text in the input field below to see its SHA-256 hash
📦 Example of a Blockchain Transaction
Imagine sending money using blockchain:
🔗 Blocks and Hashes:
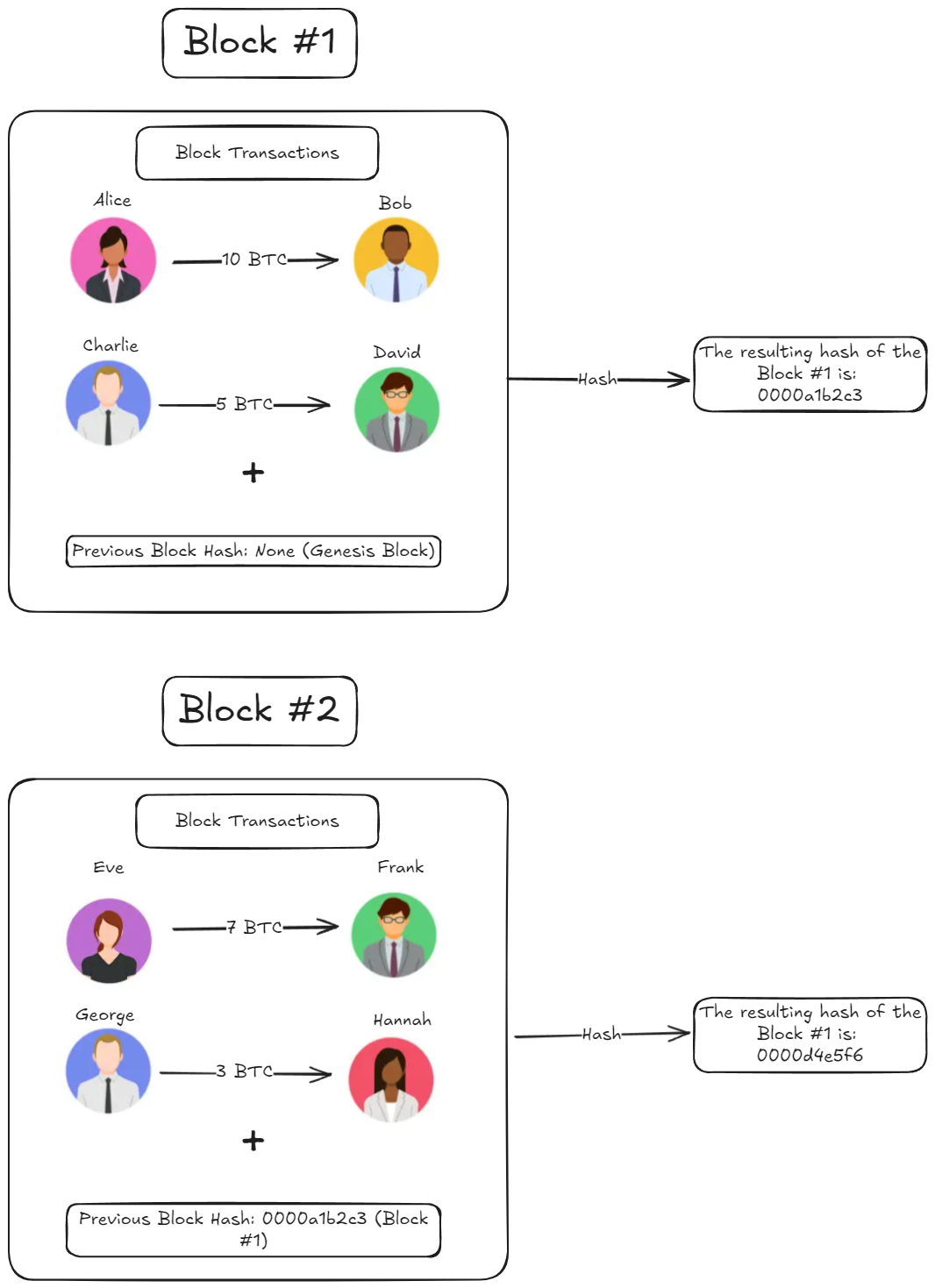
🔍 Why are hashes important for Blockchain Security?
The hashing process allows and immutable and tamper-proof ledger in a decentralized way, something revolutionary that prevented malicious actors to spend funds they don't have. ✅ Immutable: Once recorded, transactions cannot be changed. ✅ Tamper-proof: Changing one block alters all subsequent blocks, making fraud nearly impossible.
🔒 Tamper-Proof Ledger
As we have seen previously each block contains:
- Transaction Data (e.g., Alice → Bob, 10 coins)
- Its Own Hash (generated using transaction data)
- Previous Block's Hash (linking blocks together)
If an attacker tries to change a transaction (e.g., changing Alice → Bob to Alice → Eve), the block’s hash will completely change due to hashing properties. Thus the nodes that had the real transactions history will know that something happened and will reject immediatley the attacker's block.
⏳ Proof of Work Makes Changes Harder
In proof-of-work blockchains (like Bitcoin), modifying one block means:
- Recalculating its hash.
- Recalculating hashes for all subsequent blocks.
- Outpacing the network’s mining power.
This requires massive computational power, making fraud impractical.
⚖️ Decentralization & Consensus
Even if an attacker controls enough power to alter hashes, the distributed network (thousands of Nodes will reject the altered blockchain in favor of the correct one. This makes extremely important to run nodes to keep the network secured.
🏆 Final Thoughts
Hashing ensures blockchain remains secure, transparent, and immutable, preventing fraud and enabling trustless transactions without central authority.
